3d printing application has been extended to archaeology and its results are remarkable. 3d printed statues of three Ancient Buddhist statues have been put on display in the Chinese city of Qingdao. The statues were originally from Yungang Grottoes which is a UNESCO World Heritage. 3d technology has been previously used to conserve the remains of Bamiyan Buddha in Afghanistan. The Yungang Grottoes Research Institute used 3d scanners to record the physical and visual data of statues and carvings. Using the 3d scanned data the replicas were 3d printed. The whole of the 3d models was printed using the method of additive manufacturing on 20 different machines at Shenzhen. The Margin of error between original work and replica was less than 5 millimeters. The color and texture were initially done by the 3d printers and finely tuned by artists.
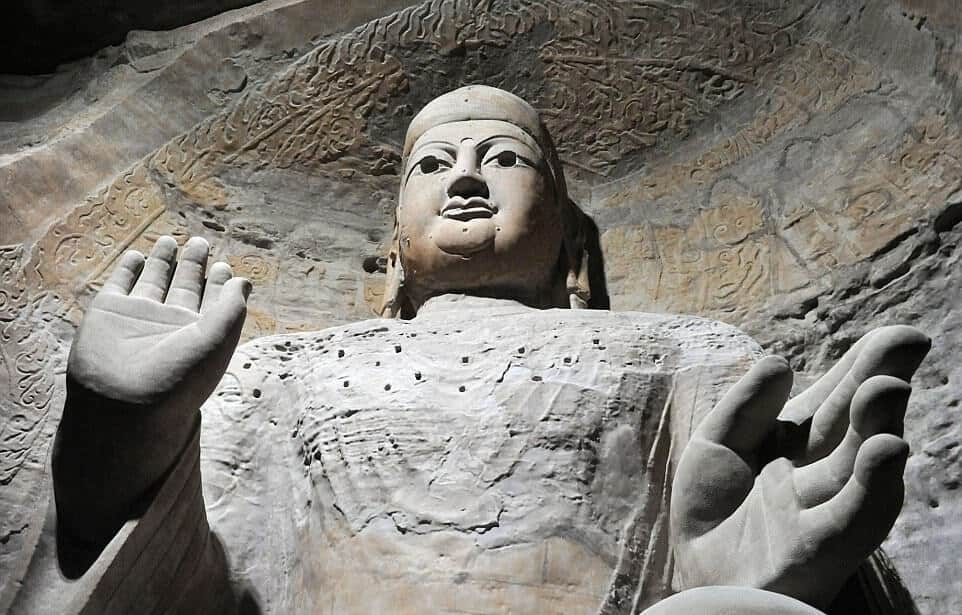

Chinese archaeologists and artists are using 3d printing to make a perfect copy of the Yungang Grottoes
Why are 3d printed statues made?
Preserving age-old statues was difficult using the earlier techniques involving physical and chemical methods but using this replication process of 3d scanning and 3d printing more such statues can be made. Zhejiang University’s Diao Changyu explains that this technology will now be used to duplicate other at-risk artifacts so that they can be protected and preserved in the coming future.
Read more: